Introduction and Definition
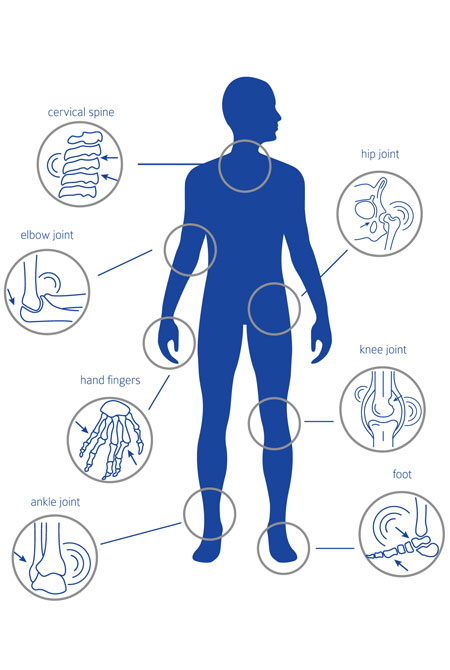
- OA (Osteoarthritis) is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease. It can occur in any synovial joint; the common sites being the knees, hips & small hand joints.
- Consequences of OA include pain, reduced function, & restriction in daily activities.
- Management is made complex because structural changes can occur without the patient displaying any symptoms.
- There are different definition of OA (Osteoarthritis)
- “Definition of OA varies, but considered to be a chronic degenerative & progressive condition affecting synovial joint.” – Carol David, 1999
- “It is a degenerative, non-inflammatory joint disease characterized by destruction of articular cartilage & formation of new bone at the joint surface & margins.” John Ebnezar, 2003
- “OA (Osteoarthritis) refers to a clinical syndrome of joint pain accompanied by varying degrees of functional limitation & reduced quality of life.” – Royal College of Physician, 2008
Incidence
- OA (Osteoarthritis) The most common reasons of disability except traumas.
- Disability, initially appears asymptomatically in the 2th and 3rd grades.
- Incidence increases by aging. Incidence rate in population is 10% and incidence rate goes up to 50% for population aged 60 and above. Incidence is highly common for population aged 80 and above with 90%
- Incidence rate usually onset in the 50s
- Mostly occurs at the ends of the fingers, knees, and hips
- Women are more commonly affected than men.